Step 1 – Install Erlang
First, use the following commands to add Erlang yum repository on RHEL based system. You can simply download Erlang repository package from its official website and install on your system. Now, you can install Erlang package on your system using the following command. This will install all of its dependencies as well.
Step 2 – Install RabbitMQ Server
After installing requirements, now download the RabbitMQ rpm package as per your operating system version from its official website. CentOS/RHEL 7 & Fedora >= 19 CentOS/RHEL 6 & Fedora < 19 After downloading the RabbitMQ server package, import rabbitmq signing key and install it using the following commands.
Step 3 – Manage RabbitMQ Service
After completing above installations, enable the RabbitMQ service on your system. Also, start the RabbitMQ service. Use one the below methods sysvinit for older systems or systemctl for the latest operating system.
Using Init – CentOS/RHEL 6 & Fedora < 19
Uisng Systemctl – CentOS/RHEL 7 & Fedora >= 19
Step 4 – Create Admin User in RabbitMQ
By default rabbitmq creates a user named “guest” with password “guest”. You can also create your own administrator account on RabbitMQ server using following commands. Change password with your own password.
Step 5 – Setup RabbitMQ Web Management Console
RabbitMQ also provides and web management console for managing the entire RabbitMQ. To enable web management console run following command on your system. The web management console helps you for managing RabbitMQ server. RabbitMQ dashboard starts on port 15672. Access your server on the port to get dashboard. Use the username and password created in step 4
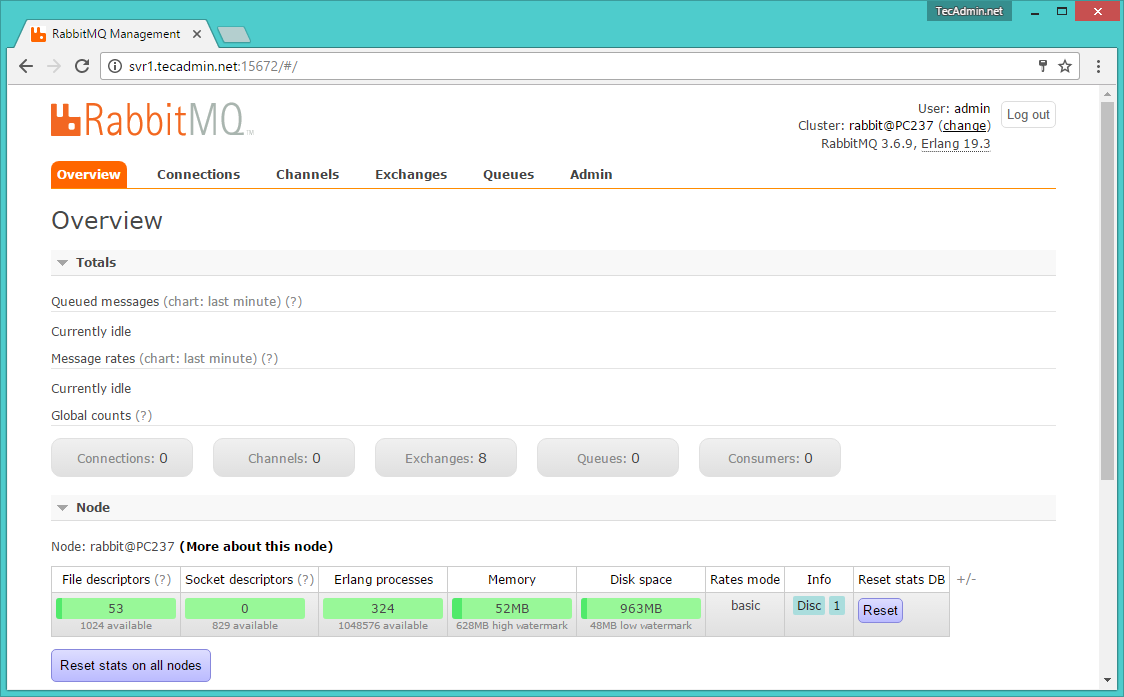
After login, you will get the RabbitMQ management web interface dashboard.