Ansible is a better alternatives of the other popular infrastructure automation tools available like Chef and Puppet. You don’t need to install any client software on nodes to manage through Ansible server. It uses SSH connection to execute tasks on nodes. This tutorial will help you to install and configure Ansible on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Linux systems.
Prerequisites
We have one control node to configure Ansible server and three node servers to be managed. Here control node is running with Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system. First and third node is running with Ubuntu 18.04 server and Second node is running with centos 7 server. Here is list of nodes with IP address and hostnames:
Control node – 10.0.1.10 (control-node) First node – 10.0.1.101 (web-host1) Second node – 10.0.1.102 (web-host2) Third node – 10.0.1.103 (db-host1) Step 1 – Setup SSH KeysYou can configure key based ssh for the remote Linux Ansible hosts. So password will not be required for SSH. Ansible also allows you to use a password for ssh, but key-based ssh is more secure.Login to the control node (10.0.1.10) and generate ssh key pair:
Just press “Enter” to all the input asked by the command. Login to the control node (10.0.1.10) and generate ssh key pair: Copy the public key to all your remote nodes you need to connect via with SSH protocols.
Step 2 – Installing Ansible on Ubuntu
You can install Ansible server from official packages repositories on Ubuntu system. Which has the latest debian packages. Execute the following command to setup Ansible PPA on your Ubuntu system. Software Updater utility will update the packages cache on your system. So you have to run the following command to install or update Ansible on your Ubuntu system Enter ‘Y’ for all the installation confirmation to complete install process. Next, you need to configure Ansible server
Step 3 – Configure Inventory File
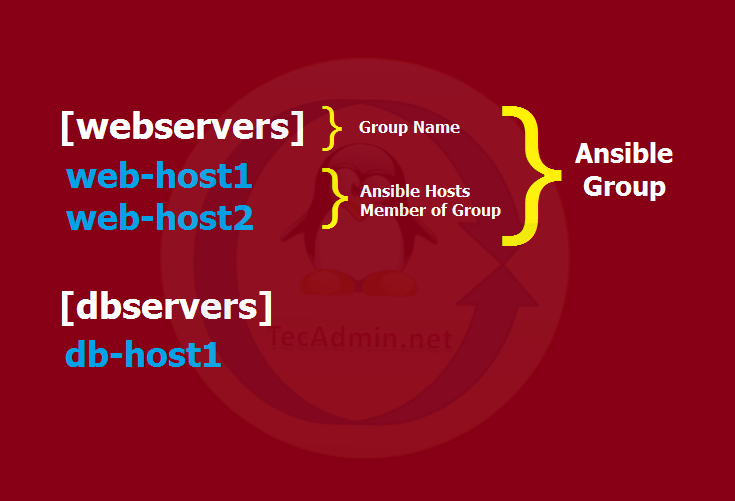
Your server is ready with Ansible for remote host management and automation. You can have a number of hosts you need and manage them with single Ansible server. Here you need to define your remote systems in Ansible hosts file (/etc/ansible/hosts). You can also make groups of hosts with similar types. Here you need to properly organize your hosts into groups. Groups are used for performing one task on all remote hosts defined under it. Edit Ansible hosts configuration file. For exmaple: Add your hosts and organize them with groups. A host can be added under multiple groups. The below image will help you to understand group and hosts under a group.
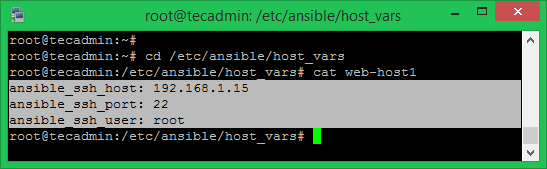
Single Host Vars Configuration
You need to define settings for your hosts. The host-specific file must be with the same name as host (eg: web-host1) under the host_vars directory. Add the SSH settings to this file for the web-host1.
In case you don’t have used Step 1 for the ssh connection for this host. You can also add one of the below methods to web-hosts1 configuration file for the authentication.
Group Vars Configuration
You can configure common variable settings of a Group under group configurations. The group file name must be same as the group name (eg: webservers) under group_vars directory. Add the common variables to this file used by all the hosts added under this group.
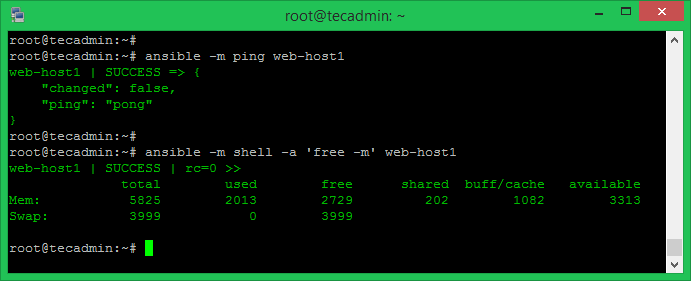
Step 4 – Testing Ansible Connection
Your Ansible is ready to use. To test all nodes connectivity use ping module. Login to your Ansible server and execute following command: You can also test connectivity for the specific host or groups. You can also run any Linux command using the Ansible shell module. For example, execute the below command to test the free memory on web-host1.
You can also perform the same task for a group. Just use group name instead of hostname.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned to install Ansible server on Ubuntu 20.04 system. Also configured remote hosts to be managed with Ansible server.